Linux 보안 자동화를 위한 Ansible 활용 실용적인 방법
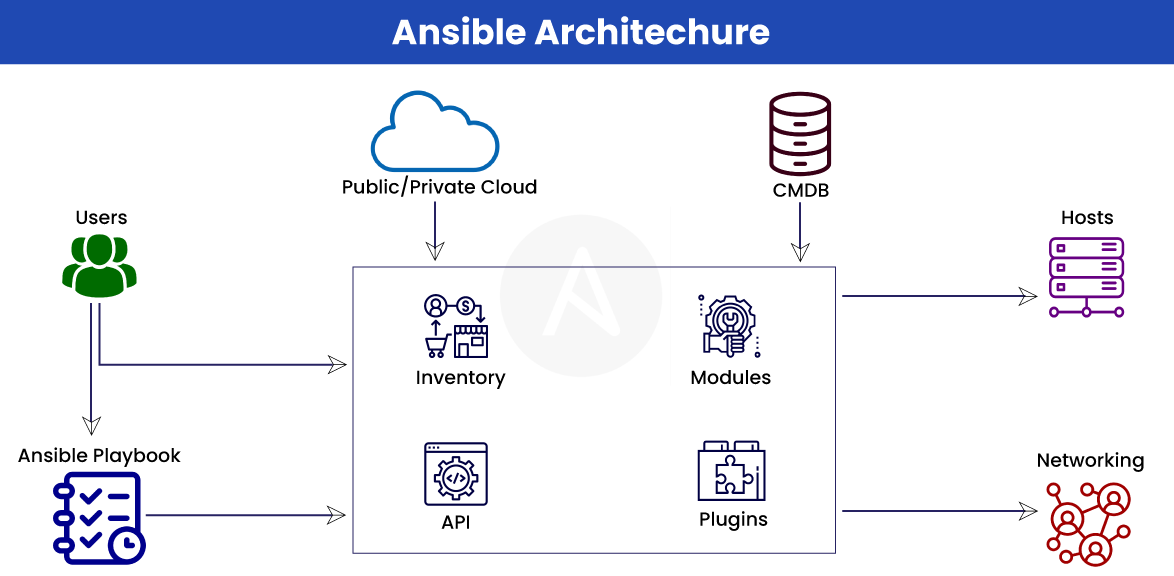
Ansible과 Linux를 통합하여 보안 자동화를 구현하면 시스템의 보안 상태를 강화하고, 관리 작업을 간소화하며, 일관된 규정을 준수할 수 있습니다. 아래는 Ansible과 Linux 보안 관리의 통합을 위한 몇 가지 실용적인 방법입니다.
1. AI 통합을 통한 향상된 자동화
AI 기반 도구를 Ansible과 통합하면 보안 자동화가 크게 향상될 수 있습니다. AI 기반 도구는 다음과 같은 작업에 도움을 줄 수 있습니다.
- 명령 해석: 자동으로 명령을 해석하고 실행합니다.
- 이상 탐지: 네트워크 트래픽이나 시스템 동작에서 비정상적인 패턴을 식별합니다.
- 예측 분석: 과거 데이터를 기반으로 잠재적인 보안 위협을 예측합니다.
- 자체 학습 자동화: 시간이 지남에 따라 보안 조치를 적응하고 개선합니다.
예제 플레이북: 이상 탐지 통합
- name: Detect anomalies and trigger actions
hosts: all
tasks:
- name: Install AI monitoring tool
apt:
name: ai-monitor
state: present
- name: Monitor system for anomalies
command: ai-monitor --scan
register: scan_output
- name: Trigger incident response
when: "'anomaly' in scan_output.stdout"
shell: |
ansible-playbook /path/to/incident_response_playbook.yml2. SIEM 시스템과의 통합
Ansible은 SIEM(Security Information and Event Management) 시스템과의 통합을 통해 보안 데이터를 자동으로 수집, 변환, 로드하는 ETL(Extraction, Transformation, Loading) 작업을 자동화할 수 있습니다. 이를 통해 최신의 종합적인 보안 데이터 분석이 가능합니다.
예제 플레이북: SIEM 통합
- name: Integrate with SIEM system
hosts: all
tasks:
- name: Collect log files
fetch:
src: /var/log/auth.log
dest: /tmp/logs/
flat: yes
- name: Normalize log data
command: normalize-logs /tmp/logs/auth.log
- name: Send logs to SIEM
command: send-to-siem /tmp/logs/auth.log3. 지속적인 보안 테스트 및 취약점 관리
정기적인 취약점 스캔과 지속적인 보안 테스트를 Ansible을 통해 자동화할 수 있습니다.
예제 플레이북: 지속적인 취약점 관리
- name: Run vulnerability scans
hosts: all
tasks:
- name: Install Nessus scanner
apt:
name: nessus
state: present
- name: Perform vulnerability scan
command: nessus scan --target {{ inventory_hostname }}
register: scan_results
- name: Report vulnerabilities
copy:
content: "{{ scan_results.stdout }}"
dest: /var/reports/vulnerability_report.txt4. 보안 설정 관리
Ansible을 사용하면 여러 Linux 서버에 대해 일관된 보안 설정을 보장할 수 있습니다.
예제 플레이북: 보안 설정
- name: Enforce secure configurations
hosts: all
tasks:
- name: Set password complexity
lineinfile:
path: /etc/security/pwquality.conf
regexp: '^minlen'
line: 'minlen = 14'
- name: Set file permissions
file:
path: /etc/passwd
owner: root
group: root
mode: '0644'
- name: Block unauthorized connections
ufw:
rule: deny
port: 22
proto: tcp5. 사고 대응 및 포렌식 분석 자동화
사고 대응 및 포렌식 분석을 자동화하면 신속한 위협 완화 및 조사가 가능합니다.
예제 플레이북: 사고 대응
- name: Incident response automation
hosts: all
tasks:
- name: Collect system logs
fetch:
src: /var/log/syslog
dest: /tmp/syslog/
flat: yes
- name: Create system snapshot
command: create-snapshot /tmp/snapshot.img
- name: Isolate compromised system
command: isolate-system {{ inventory_hostname }}6. 패치 관리
패치 관리를 자동화하면 시스템이 최신 보안 패치로 업데이트되어 취약점 노출을 줄일 수 있습니다.
예제 플레이북: 패치 관리
- name: Automate patch management
hosts: all
tasks:
- name: Update package lists
apt:
update_cache: yes
- name: Upgrade all packages
apt:
upgrade: dist
- name: Reboot if required
reboot:
when: apt_result.changed7. 규정 준수 모니터링
Ansible과 보안 모니터링 기술을 결합하여 규정 준수 모니터링 작업을 자동화할 수 있습니다. 시스템 설정을 산업 표준 및 법적 요구사항과 비교하여 규정 준수를 보장하고 잠재적인 보안 취약점을 식별합니다.
예제 플레이북: 규정 준수 모니터링
- name: Compliance monitoring
hosts: all
tasks:
- name: Check password policy compliance
command: check-password-policy
register: compliance_check
- name: Report compliance status
copy:
content: "{{ compliance_check.stdout }}"
dest: /var/reports/compliance_report.txtAnsible을 Linux 보안 자동화와 통합하면 조직의 보안 태세를 크게 강화할 수 있습니다. 설정 관리, 취약점 스캔, 사고 대응, 규정 준수 모니터링 등의 작업을 자동화하여 일관되고 효율적인 보안 접근 방식을 보장하고, 인간 오류의 위험을 줄이며, 잠재적인 위협에 대한 대응 시간을 개선할 수 있습니다.
리눅스 시스템에서 위와 같은 상태 외에 /var/log/secure 및 /var/log/messages 로그를 Elasticsearch로 수집하는 방법은 Filebeat를 사용하면 간편하게 설정할 수 있습니다. Filebeat는 로그 파일을 읽고, Elasticsearch로 전송하는 경량 로그 전송기입니다. 아래 단계에 따라 설정을 진행할 수 있습니다.
1. Filebeat 설치
CentOS/RHEL
sudo rpm --import https://packages.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch
sudo vi /etc/yum.repos.d/elastic.repoelastic.repo 파일에 다음 내용을 추가하세요.
[elastic-7.x]
name=Elastic repository for 7.x packages
baseurl=https://artifacts.elastic.co/packages/7.x/yum
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch
enabled=1
autorefresh=1
type=rpm-md그런 다음 Filebeat를 설치합니다.
sudo yum install filebeatUbuntu/Debian
wget -qO - https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch | sudo apt-key add -
sudo apt-get install apt-transport-https
echo "deb https://artifacts.elastic.co/packages/7.x/apt stable main" | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/elastic-7.x.list
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install filebeat2. Filebeat 설정
Filebeat 설정 파일을 편집하여 /var/log/secure 및 /var/log/messages 로그 파일을 모니터링하도록 설정합니다.
sudo vi /etc/filebeat/filebeat.yml파일의 filebeat.inputs 섹션에 다음을 추가하세요.
filebeat.inputs:
- type: log
enabled: true
paths:
- /var/log/secure
- /var/log/messagesoutput.elasticsearch 섹션을 찾아 Elasticsearch 클러스터 정보를 입력합니다.
output.elasticsearch:
hosts: ["http://localhost:9200"]
username: "elastic"
password: "password"위의 username과 password는 실제 Elasticsearch 설정에 맞게 변경합니다.
3. Filebeat 시작 및 활성화
Filebeat를 시작하고 부팅 시 자동으로 시작되도록 설정합니다.
sudo systemctl start filebeat
sudo systemctl enable filebeat4. Elasticsearch에서 인덱스 생성 확인
Filebeat가 정상적으로 작동하면 Elasticsearch에서 인덱스가 생성되는지 확인합니다.
curl -X GET "localhost:9200/_cat/indices?v"이제 /var/log/secure 및 /var/log/messages 로그 파일이 Elasticsearch로 수집되고 있는지 Kibana에서 확인할 수 있습니다. Kibana를 사용하여 시각화를 설정하고 로그를 분석할 수 있습니다.
위 과정에서 문제가 발생하면 Filebeat 로그를 확인하여 문제를 해결합니다.
sudo tail -f /var/log/filebeat/filebeat추가 설정 및 보안 고려사항
- TLS 설정: Elasticsearch와의 통신을 TLS로 암호화하는 것이 좋습니다.
- 인덱스 관리: 로그 양이 많을 경우 인덱스 관리를 통해 성능을 최적화합니다.
- 사용자 및 역할 관리: Elasticsearch의 보안 설정을 통해 적절한 권한을 부여합니다.
이 과정은 기본적인 설정 방법을 다루며, 실제 환경에 맞게 추가적인 설정이 필요할 수 있습니다.